Azure Site Recovery (ASR) is a powerful disaster recovery and business continuity solution provided by Microsoft Azure. It enables businesses to keep their critical applications and services up and running in the event of unexpected downtime, disasters, or disruptions. With ASR, you can replicate your on-premises virtual machines, physical servers, and even entire data centers to Azure, and quickly restore them when needed.
Azure Site Recovery (ASR) is a powerful disaster recovery and business continuity solution provided by Microsoft Azure. It enables businesses to keep their critical applications and services up and running in the event of unexpected downtime, disasters, or disruptions. With ASR, you can replicate your on-premises virtual machines, physical servers, and even entire data centers to Azure, and quickly restore them when needed.
In this blog post, we will dive deep into the capabilities, benefits, and use cases of Azure Site Recovery. We will also explore the key features, architecture, and pricing model of ASR.
Capabilities of Azure Site Recovery
Azure Site Recovery provides a range of capabilities that can help businesses ensure high availability, data protection, and disaster recovery. Here are some of the key capabilities of ASR:
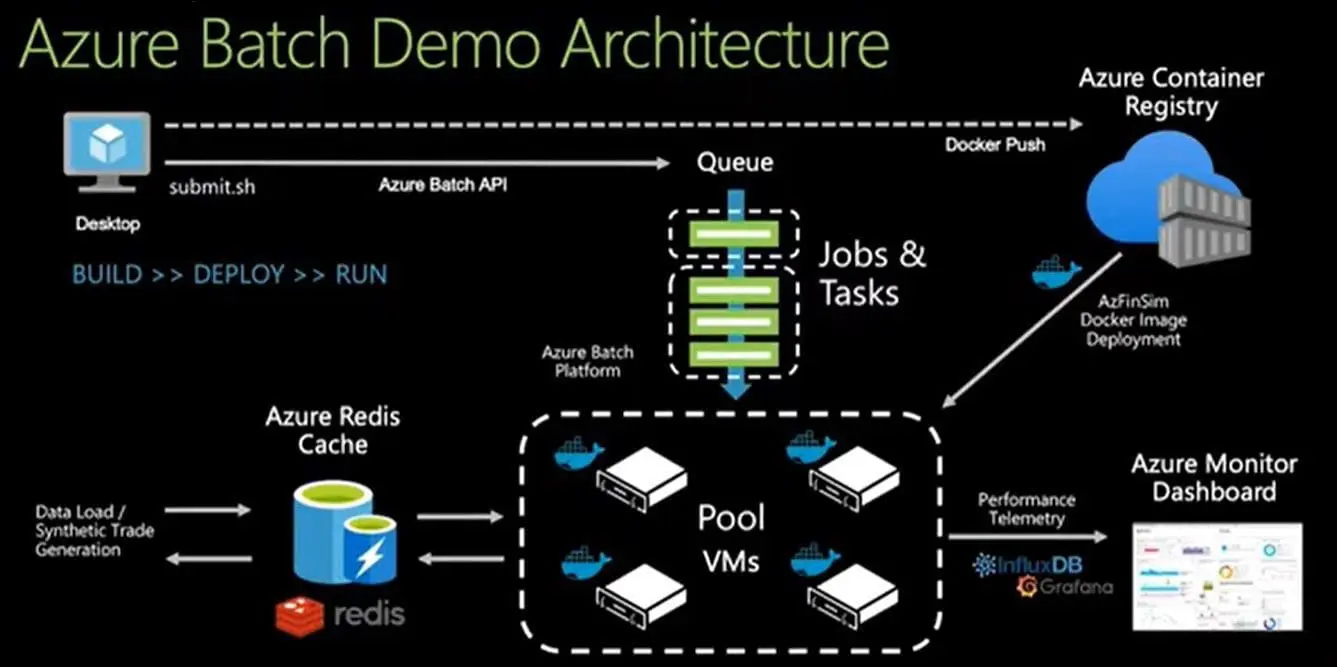
- Replication: ASR can replicate virtual machines, physical servers, and even entire data centers to Azure. This enables businesses to keep their critical applications and services up and running in the event of unexpected downtime, disasters, or disruptions.
- Orchestration: ASR can orchestrate the failover and failback of replicated virtual machines and servers. This ensures that the entire failover process is automated, orchestrated, and monitored.
- Testing: ASR provides a non-disruptive way to test disaster recovery scenarios without impacting the production environment. This enables businesses to validate their disaster recovery plans and ensure that they are working as expected.
- Integration: ASR integrates with a range of Azure services, including Azure Backup, Azure Monitor, Azure Automation, and Azure Security Center. This enables businesses to have a holistic view of their disaster recovery and business continuity operations.
Benefits of Azure Site Recovery
Azure Site Recovery provides a range of benefits to businesses of all sizes and industries. Here are some of the key benefits of ASR:
- High availability: ASR enables businesses to achieve high availability of their critical applications and services. This ensures that their customers and employees have access to the applications and services they need, even in the event of unexpected downtime, disasters, or disruptions.
- Data protection: ASR ensures that data is protected and can be recovered in the event of data loss or corruption. This is essential for businesses that handle sensitive data or have compliance requirements.
- Reduced downtime: ASR can help businesses reduce downtime by providing a fast and efficient way to recover from disasters or disruptions. This can save businesses a significant amount of time, money, and resources.
- Simplified disaster recovery: ASR simplifies the disaster recovery process by automating failover and failback operations. This reduces the risk of human error and ensures that the entire process is orchestrated and monitored.
- Lower costs: ASR can help businesses reduce their disaster recovery costs by eliminating the need for expensive hardware and infrastructure. This is because businesses can replicate their virtual machines and servers to Azure, which provides a cost-effective disaster recovery solution.
Use cases for Azure Site Recovery
- Business Continuity: ASR can help businesses ensure business continuity by providing a way to keep their critical applications and services up and running in the event of unexpected downtime, disasters, or disruptions. With ASR, businesses can replicate their on-premises virtual machines and servers to Azure and failover to them in the event of a disaster.
- Data Protection: ASR can help businesses protect their data by replicating it to Azure and providing a way to recover it in the event of data loss or corruption. With ASR, businesses can set up a replication policy to replicate data to Azure and configure recovery points to restore data to a specific point in time.
- Migration: ASR can be used to migrate virtual machines and servers from on-premises to Azure. With ASR, businesses can replicate their on-premises workloads to Azure and then failover to the replicated virtual machines in Azure. This can help businesses move their workloads to Azure in a seamless and efficient manner.
- Testing: ASR provides a non-disruptive way to test disaster recovery scenarios without impacting the production environment. With ASR, businesses can test their disaster recovery plans and ensure that they are working as expected without interrupting their production environment.
- DevOps: ASR can be used in DevOps scenarios to replicate development and test environments to Azure. This can help businesses reduce the time and cost of setting up and managing these environments. With ASR, businesses can replicate their development and test environments to Azure and then failover to them when needed.
- Compliance: ASR can help businesses meet compliance requirements by ensuring that their data is protected and can be recovered in the event of data loss or corruption. With ASR, businesses can replicate their data to Azure and then configure recovery points to ensure that their data can be restored to a specific point in time.
- Hybrid Cloud: ASR can be used in hybrid cloud scenarios to ensure high availability and disaster recovery across on-premises and Azure environments. With ASR, businesses can replicate their on-premises workloads to Azure and then failover to them in the event of a disaster.
- Multi-Site Disaster Recovery: ASR can be used to provide disaster recovery across multiple sites. With ASR, businesses can replicate their virtual machines and servers to multiple Azure regions and then failover to the replicated virtual machines in the event of a disaster.
In summary, Azure Site Recovery provides a range of capabilities that can help businesses ensure high availability, data protection, and disaster recovery. It can be used in a wide range of use cases across different industries to provide a cost-effective and efficient disaster recovery solution.
Until next time,
Rob