 In an age where cyber threats are an unfortunate part of daily digital life, protecting your online accounts is paramount. I get asked or hear about a relative/friend getting hacked because of just having a simple or easily crackable password. One of the most effective ways to bolster your online security is through Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), often referred to as Two-Factor Authentication (2FA). In this post, we’ll dive into the importance of MFA and guide you on activating it on popular social media platforms: LinkedIn and Facebook.
In an age where cyber threats are an unfortunate part of daily digital life, protecting your online accounts is paramount. I get asked or hear about a relative/friend getting hacked because of just having a simple or easily crackable password. One of the most effective ways to bolster your online security is through Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), often referred to as Two-Factor Authentication (2FA). In this post, we’ll dive into the importance of MFA and guide you on activating it on popular social media platforms: LinkedIn and Facebook.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication?
Multi-Factor Authentication is a security measure that requires users to present two or more forms of identification before accessing their accounts. This can include something you know (like a password), something you have (like a mobile device), and something you are (like a fingerprint).
MFA adds a layer of security to the standard username/password model, making it significantly more difficult for unauthorized users to access your accounts. Even if a hacker obtains your password, they must bypass the second (or third) authentication factor, which is typically much more challenging.
Why is Multi-Factor Authentication Important?
In an era where data breaches are increasingly common, MFA provides enhanced security for your digital accounts. Here are a few key reasons why MFA is essential:
1. Enhanced Security: As discussed, MFA makes it much harder for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access to your account. Even if they crack your password, they must overcome the additional authentication factor(s).
2. Data Protection: By securing your account with MFA, you protect your budget and personal and professional data. This is particularly important for business accounts, which often contain sensitive data.
3. Minimized Risk of Identity Theft: Cybercriminals often use stolen account information to impersonate the account holder, leading to identity theft. By using MFA, you can significantly reduce this risk.
4. Compliance with Industry Standards: Many industries require MFA to meet security standards and regulations. For example, businesses handling credit card data must comply with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which mandates MFA.
Now that we understand MFA’s importance let’s look at how to enable it on LinkedIn and Facebook.
Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication on LinkedIn
On the LinkedIn Website
- Click on your avatar in the top-right corner of the LinkedIn website. In the open menu, click the “Settings & Privacy” option.
Click on the Account tab, scroll down to the “Two-Step Verification” section, and click the “Change” link. 3. The section will expand. Click the “Turn On” button.
- You can choose whether to use an authenticator app to generate a code for you or to receive SMS (text) messages with the code. Select your preferred method, and then click the “Continue” button.
- Enter your password in the prompt that appears and then click “Done.”
- The instructions for adding an account to your authenticator app are displayed. Add a new account in your authenticator app, scan the QR code using your phone’s camera, and once the account is created, enter the six-digit code from the authenticator app into the text box in LinkedIn and click “Continue.”
- Two-factor authentication is now turned on. Click on “Recovery Codes” to display the backup codes, so you can still get in if you ever lose your phone.
- Click “Copy Codes” and save them somewhere secure. If you ever lose or wipe your phone, you’ll need them to get into your LinkedIn account.
- Now that you’ve turned on two-factor authentication, you must log in again through any other devices you use, such as your phone.

On the LinkedIn Mobile App
- Open the LinkedIn app and tap your profile picture.
- Then select the “View Profile” link.
- Tap on the Settings gear in the top-right corner.
- Open the “Privacy” tab, scroll down, and tap “Two-Step Verification.”
- Select the “Set Up” button.
- Choose whether to use an authenticator app to generate a code for you or to receive SMS (text) messages with the code. Select your method and tap “Continue.”
- Enter your password in the prompt that appears and then tap the “Submit” button.
- The instructions for adding an account to your authenticator app are displayed. Add a new account to your authenticator app and tap “Continue.”
- Enter the six-digit code from the authenticator app into the text box in LinkedIn and tap “Verify.”
- Two-factor authentication is now turned on. You won’t have to enter the two-factor code on your phone, although you will have to enter it if you access LinkedIn on any other device.
- Tap the “Recovery Codes” link to display the backup codes, so you can still get in if you ever lose your phone.
- Tap “Copy Codes” and save them somewhere secure. If you ever lose or wipe your phone, you’ll need them to get into your LinkedIn account.
- Now that you’ve turned on two-factor authentication, you must log in again on any other devices you own using the two-factor code.
Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication on Facebook
On Facebook Web Browser
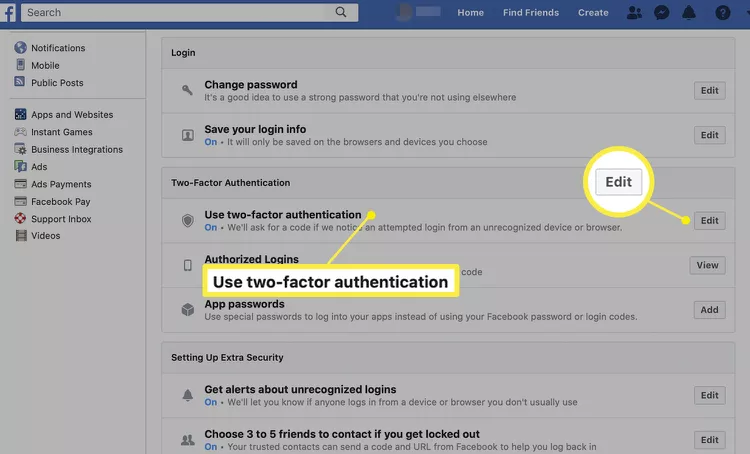
- Log into Facebook and select the downward arrow icon in the top-right section, then Choose Settings & Privacy.
- Click on Settings.
- Choose Security & Login in the left-hand menu.
- Scroll down and click on Use two-factor authentication.
- Click on Use text message (SMS), then follow the prompts and assign the contact to receive your 2FA codes. Now, anytime you log into Facebook, you must verify a random code sent to that security method. But do beware; if you do not have access to that method, you may be unable to log into your Facebook account in the future.
On the Facebook Mobile App (Android)
- Open the Facebook app and tap on the three horizontal lines in the upper right-hand corner. Then, tap on Settings & Privacy, and then choose Settings.
- Select Security and Login.
- Tap on Use two-factor authentication.
- Choose the option to turn 2FA on. Then, verify that it is on (it gives you the option to turn it off).
On the Facebook Mobile App (iOS)
- Open the Facebook app on your iPhone and tap on the three horizontal lines in the lower right-hand corner.
- Select Settings & Privacy, followed by Settings.
- Choose Security and Login.
- Tap on Use two-factor authentication.
- Tap Turn On or Turn Off to enable or disable 2FA. After you’ve enabled 2FA, verify that the phone number is one where you can receive text messages and alerts.
Conclusion
Multi-Factor Authentication is a simple yet powerful method to add an extra layer of security to your online accounts. Requiring additional information beyond just your password makes it significantly harder for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access to your accounts. Whether it’s a code sent to your phone via SMS or a code generated by an authentication app, this additional step can deter potential attacks and protect your personal and professional information from being compromised.
While it might seem inconvenient sometimes, the peace of mind it provides by safeguarding your digital identity and data is invaluable. The extra time it takes to enter a second factor of authentication is nothing compared to the time and stress caused by dealing with a compromised account. Considering the rising threats of cyber attacks, phishing attempts, and data breaches, Multi-Factor Authentication is no longer an option but a necessity for online security.
Remember that each layer of security you add makes it exponentially harder for anyone to break into your account. With Multi-Factor Authentication, even if someone manages to guess or steal your password, they would still need your phone or access to your email account to get in. This is a significant hurdle for cybercriminals and can be enough to deter many types of attacks.
While MFA significantly improves your account’s security, it’s also important to note that it’s not a silver bullet. It should be part of a comprehensive approach to online security that includes using strong, unique passwords, being careful about the personal information you share online, and being aware of the latest phishing and scam tactics.
As demonstrated above, enabling MFA on popular platforms like LinkedIn and Facebook is straightforward and doesn’t require any technical expertise. So, if you haven’t done so already, take a few moments to turn on MFA for your accounts and add an essential layer of security to your online presence. In today’s digital age, it’s not just about protecting your accounts; it’s about protecting your identity, personal information, and, ultimately, your peace of mind.
Until next time,
Rob

 TikTok, a social media platform owned by ByteDance, a Beijing-based company, has taken the world by storm. Its short-form video content has attracted millions of users, particularly among the younger generation. However, as with any technology, it comes with its own set of risks and concerns. This blog post will delve into the technical dangers associated with TikTok, including data privacy, censorship, and potential misuse of the platform.
TikTok, a social media platform owned by ByteDance, a Beijing-based company, has taken the world by storm. Its short-form video content has attracted millions of users, particularly among the younger generation. However, as with any technology, it comes with its own set of risks and concerns. This blog post will delve into the technical dangers associated with TikTok, including data privacy, censorship, and potential misuse of the platform.